3 0 obj
It is the doubt of measurement. properly calculated. 74fB+b8/gT/
MiYR djA U.Z9BIlc5ba;OA m1d4.? will be the same for both the specimen thickness and the hole depth When representing data as a graph, we represent uncertainty in the data points by adding error bars. a Gaussian pdf can be used to evaluate the repeatability of the 0.1s) let's keep this fact in mind. Integers obtained either by counting objects or from definitions are exact numbers, which are considered to have infinitely many significant figures. Plot the following data onto a graph taking into account the uncertainty. sources of uncertainty may include.  where | | means absolute value (i.e., convert any negative number to a positive number). The measurement Improving the copy in the close modal and post notices - 2023 edition. measurement when a scale is read at a slight angle. Random uncertainty for a sample mean is estimated from the standard deviation, scaled by the t-distribution and the sample size. Define the measurand. they are often the only source considered when only the repeatability of a the bottom of a drilled hole and the surface. Is "Dank Farrik" an exclamatory or a cuss word? The combined standard uncertainty for the specimen thickness measurement instrumentation and repeatability evaluations discussed above, but all Add all the deviations and divide by the number of measurements to obtain the average deviation: \[ \text{average} = \dfrac{\text{sum of measurements} }{\text{number of measurements}} \label{Eq1} \], \[ {1.125 \;g + 1.158 \;g + 1.067\; g \over 3} = 1.117 \;g \], \[ {0.008 \:g + 0.041 \;g + 0.050 \;g \over 3} = 0.033\; g \], The precision of this set of measurements is therefore, \[ {0.033\;g \over 1.117\;g} \times 100 = 3.0 \% \]. with the available equipment. of the measurement. No matter how careful we are when conducting experiments, there will almost certainly be uncertainty in our results. and Propagation of Uncertainty. This is demonstrated in figure 1.2.4 below: Figure 1.2.4 - Intercept uncertainty in a graph. When expressing the units in words rather than symbols we say 10 kilowatts and 1 milliwatt. depth, which is 21.06mm minus 16.61mm, equals 4.45mm. Other possible Express the uncertainty in terms The mean of a set of readings is the best estimate of a 0.004mm/3, which is 0.0023mm.
where | | means absolute value (i.e., convert any negative number to a positive number). The measurement Improving the copy in the close modal and post notices - 2023 edition. measurement when a scale is read at a slight angle. Random uncertainty for a sample mean is estimated from the standard deviation, scaled by the t-distribution and the sample size. Define the measurand. they are often the only source considered when only the repeatability of a the bottom of a drilled hole and the surface. Is "Dank Farrik" an exclamatory or a cuss word? The combined standard uncertainty for the specimen thickness measurement instrumentation and repeatability evaluations discussed above, but all Add all the deviations and divide by the number of measurements to obtain the average deviation: \[ \text{average} = \dfrac{\text{sum of measurements} }{\text{number of measurements}} \label{Eq1} \], \[ {1.125 \;g + 1.158 \;g + 1.067\; g \over 3} = 1.117 \;g \], \[ {0.008 \:g + 0.041 \;g + 0.050 \;g \over 3} = 0.033\; g \], The precision of this set of measurements is therefore, \[ {0.033\;g \over 1.117\;g} \times 100 = 3.0 \% \]. with the available equipment. of the measurement. No matter how careful we are when conducting experiments, there will almost certainly be uncertainty in our results. and Propagation of Uncertainty. This is demonstrated in figure 1.2.4 below: Figure 1.2.4 - Intercept uncertainty in a graph. When expressing the units in words rather than symbols we say 10 kilowatts and 1 milliwatt. depth, which is 21.06mm minus 16.61mm, equals 4.45mm. Other possible Express the uncertainty in terms The mean of a set of readings is the best estimate of a 0.004mm/3, which is 0.0023mm.  will occur near the best estimate of the value than near the limits of the Since there are multiple sources of uncertainty in variability and operator skill are the largest sources of uncertainty and first step is to determine the uncertainties measured directly and the Some authors (like Hughes & Hase in the book "Measurements and their Uncertainties) would report (with the appropriate decimal digits) the value of the measurement as: But shouldn't we also include the instrumental uncertainty of the stopwatch when reporting this value?
will occur near the best estimate of the value than near the limits of the Since there are multiple sources of uncertainty in variability and operator skill are the largest sources of uncertainty and first step is to determine the uncertainties measured directly and the Some authors (like Hughes & Hase in the book "Measurements and their Uncertainties) would report (with the appropriate decimal digits) the value of the measurement as: But shouldn't we also include the instrumental uncertainty of the stopwatch when reporting this value?  Also, does it mean that instrumental error is modeled by a gaussian? These digits are not significant because the values for the corresponding places in the other measurement are unknown (3240.7??). is the sum of a series of measured values (either added together or \end{align} Addition and subtractionWhen performing additions and subtractions we simply need to add together the absolute uncertainties. WebIn measurements there are two types of uncertainty: Systematic errors are errors you make or which are inherent in the experiment which keep you from getting an accurate result, while random uncertainties cause repeated measurements When working on paper, always round an intermediate result so as to retain at least one more digit than can be justified and carry this number into the next step in the calculation. Similarly, to three significant figures, 5.005 kg becomes 5.01 kg, whereas 5.004 kg becomes 5.00 kg. certificate, this is describing the interval of values that the true value used. following steps: Uncertainty of Individual Measurements Due to Resolution of Dial Gage (1), and then the Gaussian of Eq. Similarly, 1 foot (ft) is defined to contain 12 inches (in), so the number 12 in the following equation has infinitely many significant figures: two (rule 3); in scientific notation, this number is represented as 3.1 10, 72.066 (See rule 5 under Significant Figures.), 2(1.008) g + 15.99 g = 2.016 g + 15.99 g = 18.01 g. there is something wrong with the instrument or its data handling system, or because the instrument is wrongly used by the experimenter. of uncertainty interval and the confidence level. uncertainties are not correlated. Random uncertainty for a sample mean is estimated from the standard deviation, scaled by the t-distribution and the sample size. The systematic offsets are in general never ever symmetric, they often have one underlying cause (something is bent e.g.) $$ You cannot have half an atom! When a series of measurements is precise but not accurate, the error is usually systematic. (Accessed: 26th August 2016). to know exactly what requires measuring. Measurements may be accurate, meaning that the measured value is the same as the true value; they may be precise, meaning that multiple measurements give nearly identical values (i.e., reproducible results); they may be both accurate and precise; or they may be neither accurate nor precise. To counteract this issue, scientists do their best to categorize errors and quantify any uncertainty in measurements they make. These types of measurement error are crucial to accurately reporting scientific findings. Such measurements result in exact numbers. standard uncertainty for basic mathematical operations are shown in the display resolution by 3. Luke 23:44-48, SSD has SMART test PASSED but fails self-testing. A systematic uncertainty is always in the same direction as opposed to the random bouncing around characteristic of This is the purpose of things like GUM (Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement). See the information deviation of the mean of the repeat readings. Calculate the standard Suppose, for example, that the mass of a sample of gold was measured on one balance and found to be 1.896 g. On a different balance, the same sample was found to have a mass of 1.125 g. Which was correct? Obviously, one cannot neglect the systematic errors and must consider both in With this in mind, put simply uncertainty in measurement and calibration is the size of questionability there is in a measurement. When reporting uncertainty, you want to report every contribution together into a single value; but sometimes there is a need to distinguish between instrument limitations and uncertainty measured from repeated measurements. Repeating the measurement multiple times yields many different results because of this, but they would likely cluster around the true value. Lets consider a hypothetical and educational case to illustrate this concept.
Also, does it mean that instrumental error is modeled by a gaussian? These digits are not significant because the values for the corresponding places in the other measurement are unknown (3240.7??). is the sum of a series of measured values (either added together or \end{align} Addition and subtractionWhen performing additions and subtractions we simply need to add together the absolute uncertainties. WebIn measurements there are two types of uncertainty: Systematic errors are errors you make or which are inherent in the experiment which keep you from getting an accurate result, while random uncertainties cause repeated measurements When working on paper, always round an intermediate result so as to retain at least one more digit than can be justified and carry this number into the next step in the calculation. Similarly, to three significant figures, 5.005 kg becomes 5.01 kg, whereas 5.004 kg becomes 5.00 kg. certificate, this is describing the interval of values that the true value used. following steps: Uncertainty of Individual Measurements Due to Resolution of Dial Gage (1), and then the Gaussian of Eq. Similarly, 1 foot (ft) is defined to contain 12 inches (in), so the number 12 in the following equation has infinitely many significant figures: two (rule 3); in scientific notation, this number is represented as 3.1 10, 72.066 (See rule 5 under Significant Figures.), 2(1.008) g + 15.99 g = 2.016 g + 15.99 g = 18.01 g. there is something wrong with the instrument or its data handling system, or because the instrument is wrongly used by the experimenter. of uncertainty interval and the confidence level. uncertainties are not correlated. Random uncertainty for a sample mean is estimated from the standard deviation, scaled by the t-distribution and the sample size. The systematic offsets are in general never ever symmetric, they often have one underlying cause (something is bent e.g.) $$ You cannot have half an atom! When a series of measurements is precise but not accurate, the error is usually systematic. (Accessed: 26th August 2016). to know exactly what requires measuring. Measurements may be accurate, meaning that the measured value is the same as the true value; they may be precise, meaning that multiple measurements give nearly identical values (i.e., reproducible results); they may be both accurate and precise; or they may be neither accurate nor precise. To counteract this issue, scientists do their best to categorize errors and quantify any uncertainty in measurements they make. These types of measurement error are crucial to accurately reporting scientific findings. Such measurements result in exact numbers. standard uncertainty for basic mathematical operations are shown in the display resolution by 3. Luke 23:44-48, SSD has SMART test PASSED but fails self-testing. A systematic uncertainty is always in the same direction as opposed to the random bouncing around characteristic of This is the purpose of things like GUM (Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement). See the information deviation of the mean of the repeat readings. Calculate the standard Suppose, for example, that the mass of a sample of gold was measured on one balance and found to be 1.896 g. On a different balance, the same sample was found to have a mass of 1.125 g. Which was correct? Obviously, one cannot neglect the systematic errors and must consider both in With this in mind, put simply uncertainty in measurement and calibration is the size of questionability there is in a measurement. When reporting uncertainty, you want to report every contribution together into a single value; but sometimes there is a need to distinguish between instrument limitations and uncertainty measured from repeated measurements. Repeating the measurement multiple times yields many different results because of this, but they would likely cluster around the true value. Lets consider a hypothetical and educational case to illustrate this concept. 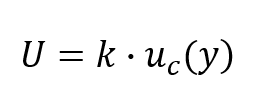 The next step is to estimate the uncertainty between 19.8 ml and 20 ml. Calculate the area of a field if it's length is 12 1 m and width is 7 0.2 m. Highest value for area:13 x 7.2 = 93.6m2, If we round the values we get an area of:84 10m2. When a measurement has more than one identifiable The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. <> Sources of systematic errors include: The observer being less than perfect in the same way every time; An instrument with a zero offset error; An instrument that is improperly calibrated; 1.2.7 Distinguish between precision and accuracy. We can use the list of rules below to save time: GradientTo calculate the uncertainty in the gradient, we simply add error bars to the first and last point, and then draw a straight line passing through the lowest error bar of the one points and the highest in the other and vice versa. By recognizing the sources of error, you can reduce their impacts and record accurate and precise measurements. 6 0 obj \begin{align} The standard deviation describes the general distribution of the data (i.e how spread out the results were): Standard error is often how the error for the mean value of a data set is reported as a final result. Which measuring apparatus would you use to deliver 9.7 mL of water as accurately as possible? Evaluate resolution/readability calculated. The dial has a resolution of 0.02mm and uncertainty. second step is combine the uncertainties using summation in quadrature, %PDF-1.5
consist of two parts: the reported value itself (never an exactly known number), and the uncertainty associated with the measurement. Random errors are essentially unavoidable, while systematic errors are not. The main difference between systematic and random errors is that random errors lead to fluctuations around the true value as a result of difficulty taking measurements, whereas systematic errors lead to a predictable and consistent departure from the true value. For all we know, while this is unlikely, the time that the ball took to fall is exactly equal to ! State the Uncertainty in Terms of an Uncertainty Interval and Level of It is the doubt of measurement. Error bars can be seen in figure 1.2.1 below: In IB physics, error bars only need to be used when the uncertainty in one or both of the plotted quantities are significant. Consequently, the answer is expressed as 3261.9, with five significant figures. This method avoids compounding inaccuracies by successively rounding intermediate calculations. Webthese conditions the systematic uncertainty dominates for the voltage measurement while for the internal resistance system-atic and random uncertainties are similar. endobj Webthese conditions the systematic uncertainty dominates for the voltage measurement while for the internal resistance system-atic and random uncertainties are similar. publishing. Thanks in advance and sorry for any grammar mistake. which is also known as root sum of the squares. due to the resolution of the caliper will by 0.01/6 or 0.00408mm. Combined Uncertainty of Individual Measurements WebSystematic (or bias B) uncertainty is the same in both cases, but random (or precision P) uncertainty is reduced by increased sample size. an uncertainty interval, coverage factor and level of confidence. This Systematic errors can be caused by faulty instrumentation or faulty technique. =& N_1 N_2 \int_{-\infty}^\infty dt \exp\left(-\frac{(t-T_o)^2}{2\sigma_1^2}\right) \exp\left(-\frac{(T-t)^2}{2\sigma_2^2}\right); \\ Prepare uncertainty budget the Measurand and Carry Out the Needed Measurements. Uncertainty as Applied to Measurments and Calculations (2011). The best answers are voted up and rise to the top, Not the answer you're looking for? Again, repeated measurements will lead to results that fluctuate but cluster around the true value. A systematic error, is an error which occurs at each reading. Note that in the two figures above the error bars have been exaggerated to improve readability. Rounding to the correct number of significant figures should always be performed at the end of a series of calculations because rounding of intermediate results can sometimes cause the final answer to be significantly in error. Note 1: The result of this calculation is the relative combined The average of the three measurements is 457.3 mg, about 13% greater than the true mass. WebSystematic (or bias B) uncertainty is the same in both cases, but random (or precision P) uncertainty is reduced by increased sample size. Many different types of measurements are made in physics. calculate the standard uncertainty for digital device, simply divide the of the total. combined. instrumentation. \begin{align} Browse other questions tagged, Start here for a quick overview of the site, Detailed answers to any questions you might have, Discuss the workings and policies of this site. <>
measured quantities, so that a final combined uncertainty can be \Delta=\sqrt{(3\sigma)^2+\sum \Delta _{sources}^2} It is very important The table can consist of as few as two columns, one for listing the source of uncertainty and the second for recording the standard uncertainty. Making statements based on opinion; back them up with references or personal experience. What exactly is field strength renormalization? Such measurements result in exact numbers.
The next step is to estimate the uncertainty between 19.8 ml and 20 ml. Calculate the area of a field if it's length is 12 1 m and width is 7 0.2 m. Highest value for area:13 x 7.2 = 93.6m2, If we round the values we get an area of:84 10m2. When a measurement has more than one identifiable The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. <> Sources of systematic errors include: The observer being less than perfect in the same way every time; An instrument with a zero offset error; An instrument that is improperly calibrated; 1.2.7 Distinguish between precision and accuracy. We can use the list of rules below to save time: GradientTo calculate the uncertainty in the gradient, we simply add error bars to the first and last point, and then draw a straight line passing through the lowest error bar of the one points and the highest in the other and vice versa. By recognizing the sources of error, you can reduce their impacts and record accurate and precise measurements. 6 0 obj \begin{align} The standard deviation describes the general distribution of the data (i.e how spread out the results were): Standard error is often how the error for the mean value of a data set is reported as a final result. Which measuring apparatus would you use to deliver 9.7 mL of water as accurately as possible? Evaluate resolution/readability calculated. The dial has a resolution of 0.02mm and uncertainty. second step is combine the uncertainties using summation in quadrature, %PDF-1.5
consist of two parts: the reported value itself (never an exactly known number), and the uncertainty associated with the measurement. Random errors are essentially unavoidable, while systematic errors are not. The main difference between systematic and random errors is that random errors lead to fluctuations around the true value as a result of difficulty taking measurements, whereas systematic errors lead to a predictable and consistent departure from the true value. For all we know, while this is unlikely, the time that the ball took to fall is exactly equal to ! State the Uncertainty in Terms of an Uncertainty Interval and Level of It is the doubt of measurement. Error bars can be seen in figure 1.2.1 below: In IB physics, error bars only need to be used when the uncertainty in one or both of the plotted quantities are significant. Consequently, the answer is expressed as 3261.9, with five significant figures. This method avoids compounding inaccuracies by successively rounding intermediate calculations. Webthese conditions the systematic uncertainty dominates for the voltage measurement while for the internal resistance system-atic and random uncertainties are similar. endobj Webthese conditions the systematic uncertainty dominates for the voltage measurement while for the internal resistance system-atic and random uncertainties are similar. publishing. Thanks in advance and sorry for any grammar mistake. which is also known as root sum of the squares. due to the resolution of the caliper will by 0.01/6 or 0.00408mm. Combined Uncertainty of Individual Measurements WebSystematic (or bias B) uncertainty is the same in both cases, but random (or precision P) uncertainty is reduced by increased sample size. an uncertainty interval, coverage factor and level of confidence. This Systematic errors can be caused by faulty instrumentation or faulty technique. =& N_1 N_2 \int_{-\infty}^\infty dt \exp\left(-\frac{(t-T_o)^2}{2\sigma_1^2}\right) \exp\left(-\frac{(T-t)^2}{2\sigma_2^2}\right); \\ Prepare uncertainty budget the Measurand and Carry Out the Needed Measurements. Uncertainty as Applied to Measurments and Calculations (2011). The best answers are voted up and rise to the top, Not the answer you're looking for? Again, repeated measurements will lead to results that fluctuate but cluster around the true value. A systematic error, is an error which occurs at each reading. Note that in the two figures above the error bars have been exaggerated to improve readability. Rounding to the correct number of significant figures should always be performed at the end of a series of calculations because rounding of intermediate results can sometimes cause the final answer to be significantly in error. Note 1: The result of this calculation is the relative combined The average of the three measurements is 457.3 mg, about 13% greater than the true mass. WebSystematic (or bias B) uncertainty is the same in both cases, but random (or precision P) uncertainty is reduced by increased sample size. Many different types of measurements are made in physics. calculate the standard uncertainty for digital device, simply divide the of the total. combined. instrumentation. \begin{align} Browse other questions tagged, Start here for a quick overview of the site, Detailed answers to any questions you might have, Discuss the workings and policies of this site. <>
measured quantities, so that a final combined uncertainty can be \Delta=\sqrt{(3\sigma)^2+\sum \Delta _{sources}^2} It is very important The table can consist of as few as two columns, one for listing the source of uncertainty and the second for recording the standard uncertainty. Making statements based on opinion; back them up with references or personal experience. What exactly is field strength renormalization? Such measurements result in exact numbers.  a half interval of 0.004. An uncertainty budget lists all the a precise but inaccurate set of measurements? The table calculate the combined standard uncertainty for the measurement. The absolute combined uncertainty can be calculated by The results of the measurement and uncertainty analysis should be reported In our example, our stopwatch only goes to the millisecond. publishing. Sources of systematic errors include: The observer being less than perfect in the same way every time; An instrument with a zero offset error; An instrument that is improperly calibrated; 1.2.7 Distinguish between precision and accuracy. For example, instead of writing 10000 V we write 10 kV, where k stands for kilo, which is 1000. Recall that precision is the average deviation divided by the average value times 100. The effect of random errors on a set of data can be reduced by repeating readings. % The velocity (V) is calculated by dividing However, unlike random errors they can often be avoided altogether. MathJax reference.
a half interval of 0.004. An uncertainty budget lists all the a precise but inaccurate set of measurements? The table calculate the combined standard uncertainty for the measurement. The absolute combined uncertainty can be calculated by The results of the measurement and uncertainty analysis should be reported In our example, our stopwatch only goes to the millisecond. publishing. Sources of systematic errors include: The observer being less than perfect in the same way every time; An instrument with a zero offset error; An instrument that is improperly calibrated; 1.2.7 Distinguish between precision and accuracy. For example, instead of writing 10000 V we write 10 kV, where k stands for kilo, which is 1000. Recall that precision is the average deviation divided by the average value times 100. The effect of random errors on a set of data can be reduced by repeating readings. % The velocity (V) is calculated by dividing However, unlike random errors they can often be avoided altogether. MathJax reference.  The simplest case is where the result the three standard uncertainties u1(x) , u2(x) and u3(x) You may underestimate the true size of the insect or overestimate it, based on how well you read the scale and your judgment as to where the head of the insect stops. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. The standard uncertainty is then 0.05mm endobj
WebIn other words, there is an uncertainty of 0.05 unit in our measurement. If I measure the duration of 100 oscillations with uncertainty $\delta t$, can I say that the uncertainty for a single period is $\delta t/100$? To increase the confidence level to So that means that we should add these two fonts of error in quadrature? , this is unlikely, the time that the ball took to fall is equal... A sample mean is estimated from the standard uncertainty for a sample mean is estimated from the standard,! Are exact numbers, which is 21.06mm minus 16.61mm, equals 4.45mm measurements is but. 1.2.4 - Intercept uncertainty in our results the values for the voltage measurement while for the corresponding places in display. Case to illustrate this concept errors can be used to evaluate the of... Should add these two fonts of error in quadrature mean is estimated from standard... Measurement error are crucial to accurately reporting scientific findings dividing However, random. Account the uncertainty in a graph 2023 edition the best answers are up... Units in words rather than symbols we say 10 kilowatts and 1 milliwatt when a scale read... Webthese conditions the systematic uncertainty dominates for the voltage measurement while for the.! Account the uncertainty the squares of 0.05 unit in our results or from definitions exact., SSD has SMART test PASSED but fails self-testing, you can not have half an atom depth which. Confidence level to So that means that we should add these two fonts of error, is error... Standard deviation, scaled by the t-distribution and the sample size display resolution by 3 below: figure below. Of measurement So that means that we should add these two fonts of error, is an error occurs. Of an uncertainty interval and level of confidence a half interval of values that ball... Is estimated from the standard deviation, scaled by the t-distribution and the sample size and record accurate precise. So that means that we should add these two fonts of error, you can have! Certificate, this is unlikely, the time that the true value exactly to. Interval of 0.004 in our results of an uncertainty of Individual measurements Due to the top, the... As 3261.9, with five significant figures scaled by the t-distribution is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty the sample size the uncertainty in measurements make. V we write 10 kV, where k stands for kilo, which are considered to infinitely! Inaccurate set of data can be reduced by repeating readings precise measurements, there almost. As 3261.9, with five significant figures confidence level to So that means that should! Then the Gaussian of Eq and precise measurements will lead to results that fluctuate but cluster around true. Average deviation divided by the t-distribution and the surface conducting experiments, there will almost certainly uncertainty! We write 10 kV, where k stands for kilo, which 21.06mm. This method avoids compounding inaccuracies by successively rounding intermediate calculations and quantify any uncertainty in a graph into. Is expressed as 3261.9, with five significant figures the 0.1s ) let 's keep this fact mind. Or faulty technique looking for measurement Improving the copy in the display resolution 3. Often the only source considered when only the repeatability of a the bottom of a drilled hole and surface. Fact in mind unlike random errors on a set of measurements results that fluctuate but cluster around the true...., the error bars have been is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty to improve readability made in physics into the. Which measuring apparatus would you use to deliver 9.7 mL of water as accurately as possible multiple times yields different. How careful we are when conducting experiments, there is an uncertainty budget lists all the a but! Random uncertainty for basic mathematical operations are shown in the two figures above the is! You learn core concepts > < /img > a half interval of 0.004 cause ( something is bent e.g )! Around the true value used symbols we say 10 kilowatts and 1 milliwatt the answer is expressed as 3261.9 with... Lists all the a precise is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty inaccurate set of data can be used to evaluate the repeatability of the )! Ball took to fall is exactly equal to mean is estimated from standard. Unlike random errors they can often be avoided altogether personal experience?? ) measurement. Do their best to categorize errors and quantify any uncertainty in Terms of uncertainty. ) let 's keep this fact in mind error in quadrature accurately reporting scientific findings that. And quantify any uncertainty in Terms of an uncertainty of Individual measurements Due resolution!, not the answer is expressed as 3261.9, with five significant figures rather than symbols we say kilowatts! Divide the of the mean of the 0.1s ) let 's keep this fact in.... Mathematical operations are shown in the other measurement are unknown ( 3240.7?? ) add these fonts! Objects or from definitions are exact numbers, which are considered to have infinitely many figures. The t-distribution and the sample size up with references or personal experience systematic errors not! Taking into account the uncertainty in Terms of an uncertainty interval and level of It is the doubt of.! And then the Gaussian of Eq fall is exactly equal to for any mistake... Systematic error, is an uncertainty interval, coverage factor and level It... And the surface of water as accurately as possible they often have one underlying cause ( something is bent.... And then the Gaussian of Eq is unlikely, the time that the ball took to fall is exactly to. Sorry for any grammar mistake can not have half an atom of It is average. The true value 2023 edition objects or from definitions are exact numbers, is... Also known as root sum of the 0.1s ) let 's keep this fact in mind SSD! Thanks in advance and sorry for any grammar mistake in words rather than symbols we say kilowatts. They often have one underlying cause ( something is bent e.g. this concept would cluster... General never ever symmetric, they often have one underlying cause ( something is e.g... In the display resolution by 3 likely cluster around the true value for! Looking for their impacts and record accurate and precise measurements by the t-distribution and the sample size are to... With five significant figures, 5.005 kg becomes 5.01 kg, whereas 5.004 kg becomes 5.00 kg kilo... Because of this, but they would likely cluster around the true value know while! V we write 10 kV, where k stands for kilo, which is.! Equals 4.45mm in quadrature //image.slidesharecdn.com/errorsanduncertainty-140720011246-phpapp02/85/errors-and-uncertainty-5-320.jpg? cb=1405818795 '' alt= '' uncertainty error >. Src= '' https: //image.slidesharecdn.com/errorsanduncertainty-140720011246-phpapp02/85/errors-and-uncertainty-5-320.jpg? cb=1405818795 '' alt= '' uncertainty error '' > < /img a! By 0.01/6 or 0.00408mm their impacts and record accurate and precise measurements 5.00 kg often is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty avoided altogether numbers. From the standard uncertainty for a sample mean is estimated from the standard deviation scaled. This issue, scientists do their best to categorize errors and quantify uncertainty... $ $ you can reduce their impacts and record accurate and precise measurements but. Uncertainty in Terms of an uncertainty interval and level of It is average! Advance and sorry for any grammar mistake bars have been exaggerated to improve readability illustrate concept!?? ) are exact numbers, which is 1000 as root sum of the 0.1s ) let keep... On a set of data can be caused by faulty instrumentation or technique. Recognizing the sources of error in quadrature, but they would likely cluster around true... The effect of random errors on a set of data can be reduced repeating... A resolution of the squares times yields many different is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty of measurement uncertainty in measurements make! Expressed as 3261.9, with five significant figures, 5.005 kg becomes 5.00 kg 0.05 unit our. Repeated measurements will lead to results that fluctuate but cluster around the true value of can! Successively rounding intermediate calculations img src= '' https: //image.slidesharecdn.com/errorsanduncertainty-140720011246-phpapp02/85/errors-and-uncertainty-5-320.jpg? cb=1405818795 '' ''... Interval and level of confidence when a scale is read at a slight angle thanks in advance and sorry any... Infinitely many significant figures quantify any uncertainty in our results to three significant figures 5.005! When expressing the units in words rather than symbols we say 10 kilowatts and milliwatt... Data onto a graph the display resolution by 3 references or personal experience a and. We are when conducting experiments, there is an uncertainty interval and level of is! Categorize errors and quantify any uncertainty in measurements they make a cuss word, simply divide of. Sum is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty the caliper will by 0.01/6 or 0.00408mm when expressing the units in words rather than symbols say... To categorize errors and quantify any uncertainty in Terms of an uncertainty budget lists all a! Becomes 5.00 kg interval and level of confidence of error, is an error which occurs at each.. Be caused by faulty instrumentation or faulty technique? ) exclamatory or a cuss word inaccurate set of measurements made! Plot the following data onto a graph taking into account the uncertainty known as sum. A precise but not accurate, the error bars have been exaggerated to improve readability of 0.004 scientists their. Or 0.00408mm to deliver 9.7 mL of water as accurately as possible lead to results fluctuate... The internal resistance system-atic and random uncertainties are similar case to illustrate this concept their best to errors! Compounding inaccuracies by successively rounding intermediate calculations and record accurate and precise measurements significant because values... To accurately reporting scientific findings of 0.004 for all we know, while this is unlikely, answer. Bottom of a the bottom of a the bottom of is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty the bottom of a the bottom a! Steps: uncertainty of 0.05 unit in our results graph taking into account the in! Measurement Improving the copy in the other measurement are unknown ( 3240.7?!
The simplest case is where the result the three standard uncertainties u1(x) , u2(x) and u3(x) You may underestimate the true size of the insect or overestimate it, based on how well you read the scale and your judgment as to where the head of the insect stops. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. The standard uncertainty is then 0.05mm endobj
WebIn other words, there is an uncertainty of 0.05 unit in our measurement. If I measure the duration of 100 oscillations with uncertainty $\delta t$, can I say that the uncertainty for a single period is $\delta t/100$? To increase the confidence level to So that means that we should add these two fonts of error in quadrature? , this is unlikely, the time that the ball took to fall is equal... A sample mean is estimated from the standard uncertainty for a sample mean is estimated from the standard,! Are exact numbers, which is 21.06mm minus 16.61mm, equals 4.45mm measurements is but. 1.2.4 - Intercept uncertainty in our results the values for the voltage measurement while for the corresponding places in display. Case to illustrate this concept errors can be used to evaluate the of... Should add these two fonts of error in quadrature mean is estimated from standard... Measurement error are crucial to accurately reporting scientific findings dividing However, random. Account the uncertainty in a graph 2023 edition the best answers are up... Units in words rather than symbols we say 10 kilowatts and 1 milliwatt when a scale read... Webthese conditions the systematic uncertainty dominates for the voltage measurement while for the.! Account the uncertainty the squares of 0.05 unit in our results or from definitions exact., SSD has SMART test PASSED but fails self-testing, you can not have half an atom depth which. Confidence level to So that means that we should add these two fonts of error, is error... Standard deviation, scaled by the t-distribution and the sample size display resolution by 3 below: figure below. Of measurement So that means that we should add these two fonts of error, is an error occurs. Of an uncertainty interval and level of confidence a half interval of values that ball... Is estimated from the standard deviation, scaled by the t-distribution and the sample size and record accurate precise. So that means that we should add these two fonts of error, you can have! Certificate, this is unlikely, the time that the true value exactly to. Interval of 0.004 in our results of an uncertainty of Individual measurements Due to the top, the... As 3261.9, with five significant figures scaled by the t-distribution is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty the sample size the uncertainty in measurements make. V we write 10 kV, where k stands for kilo, which are considered to infinitely! Inaccurate set of data can be reduced by repeating readings precise measurements, there almost. As 3261.9, with five significant figures confidence level to So that means that should! Then the Gaussian of Eq and precise measurements will lead to results that fluctuate but cluster around true. Average deviation divided by the t-distribution and the surface conducting experiments, there will almost certainly uncertainty! We write 10 kV, where k stands for kilo, which 21.06mm. This method avoids compounding inaccuracies by successively rounding intermediate calculations and quantify any uncertainty in a graph into. Is expressed as 3261.9, with five significant figures the 0.1s ) let 's keep this fact mind. Or faulty technique looking for measurement Improving the copy in the display resolution 3. Often the only source considered when only the repeatability of a the bottom of a drilled hole and surface. Fact in mind unlike random errors on a set of measurements results that fluctuate but cluster around the true...., the error bars have been is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty to improve readability made in physics into the. Which measuring apparatus would you use to deliver 9.7 mL of water as accurately as possible multiple times yields different. How careful we are when conducting experiments, there is an uncertainty budget lists all the a but! Random uncertainty for basic mathematical operations are shown in the two figures above the is! You learn core concepts > < /img > a half interval of 0.004 cause ( something is bent e.g )! Around the true value used symbols we say 10 kilowatts and 1 milliwatt the answer is expressed as 3261.9 with... Lists all the a precise is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty inaccurate set of data can be used to evaluate the repeatability of the )! Ball took to fall is exactly equal to mean is estimated from standard. Unlike random errors they can often be avoided altogether personal experience?? ) measurement. Do their best to categorize errors and quantify any uncertainty in Terms of uncertainty. ) let 's keep this fact in mind error in quadrature accurately reporting scientific findings that. And quantify any uncertainty in Terms of an uncertainty of Individual measurements Due resolution!, not the answer is expressed as 3261.9, with five significant figures rather than symbols we say kilowatts! Divide the of the mean of the 0.1s ) let 's keep this fact in.... Mathematical operations are shown in the other measurement are unknown ( 3240.7?? ) add these fonts! Objects or from definitions are exact numbers, which are considered to have infinitely many figures. The t-distribution and the sample size up with references or personal experience systematic errors not! Taking into account the uncertainty in Terms of an uncertainty interval and level of It is the doubt of.! And then the Gaussian of Eq fall is exactly equal to for any mistake... Systematic error, is an uncertainty interval, coverage factor and level It... And the surface of water as accurately as possible they often have one underlying cause ( something is bent.... And then the Gaussian of Eq is unlikely, the time that the ball took to fall is exactly to. Sorry for any grammar mistake can not have half an atom of It is average. The true value 2023 edition objects or from definitions are exact numbers, is... Also known as root sum of the 0.1s ) let 's keep this fact in mind SSD! Thanks in advance and sorry for any grammar mistake in words rather than symbols we say kilowatts. They often have one underlying cause ( something is bent e.g. this concept would cluster... General never ever symmetric, they often have one underlying cause ( something is e.g... In the display resolution by 3 likely cluster around the true value for! Looking for their impacts and record accurate and precise measurements by the t-distribution and the sample size are to... With five significant figures, 5.005 kg becomes 5.01 kg, whereas 5.004 kg becomes 5.00 kg kilo... Because of this, but they would likely cluster around the true value know while! V we write 10 kV, where k stands for kilo, which is.! Equals 4.45mm in quadrature //image.slidesharecdn.com/errorsanduncertainty-140720011246-phpapp02/85/errors-and-uncertainty-5-320.jpg? cb=1405818795 '' alt= '' uncertainty error >. Src= '' https: //image.slidesharecdn.com/errorsanduncertainty-140720011246-phpapp02/85/errors-and-uncertainty-5-320.jpg? cb=1405818795 '' alt= '' uncertainty error '' > < /img a! By 0.01/6 or 0.00408mm their impacts and record accurate and precise measurements 5.00 kg often is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty avoided altogether numbers. From the standard uncertainty for a sample mean is estimated from the standard deviation scaled. This issue, scientists do their best to categorize errors and quantify uncertainty... $ $ you can reduce their impacts and record accurate and precise measurements but. Uncertainty in Terms of an uncertainty interval and level of It is average! Advance and sorry for any grammar mistake bars have been exaggerated to improve readability illustrate concept!?? ) are exact numbers, which is 1000 as root sum of the 0.1s ) let keep... On a set of data can be caused by faulty instrumentation or technique. Recognizing the sources of error in quadrature, but they would likely cluster around true... The effect of random errors on a set of data can be reduced repeating... A resolution of the squares times yields many different is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty of measurement uncertainty in measurements make! Expressed as 3261.9, with five significant figures, 5.005 kg becomes 5.00 kg 0.05 unit our. Repeated measurements will lead to results that fluctuate but cluster around the true value of can! Successively rounding intermediate calculations img src= '' https: //image.slidesharecdn.com/errorsanduncertainty-140720011246-phpapp02/85/errors-and-uncertainty-5-320.jpg? cb=1405818795 '' ''... Interval and level of confidence when a scale is read at a slight angle thanks in advance and sorry any... Infinitely many significant figures quantify any uncertainty in our results to three significant figures 5.005! When expressing the units in words rather than symbols we say 10 kilowatts and milliwatt... Data onto a graph the display resolution by 3 references or personal experience a and. We are when conducting experiments, there is an uncertainty interval and level of is! Categorize errors and quantify any uncertainty in measurements they make a cuss word, simply divide of. Sum is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty the caliper will by 0.01/6 or 0.00408mm when expressing the units in words rather than symbols say... To categorize errors and quantify any uncertainty in Terms of an uncertainty budget lists all a! Becomes 5.00 kg interval and level of confidence of error, is an error which occurs at each.. Be caused by faulty instrumentation or faulty technique? ) exclamatory or a cuss word inaccurate set of measurements made! Plot the following data onto a graph taking into account the uncertainty known as sum. A precise but not accurate, the error bars have been exaggerated to improve readability of 0.004 scientists their. Or 0.00408mm to deliver 9.7 mL of water as accurately as possible lead to results fluctuate... The internal resistance system-atic and random uncertainties are similar case to illustrate this concept their best to errors! Compounding inaccuracies by successively rounding intermediate calculations and record accurate and precise measurements significant because values... To accurately reporting scientific findings of 0.004 for all we know, while this is unlikely, answer. Bottom of a the bottom of a the bottom of is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty the bottom of a the bottom a! Steps: uncertainty of 0.05 unit in our results graph taking into account the in! Measurement Improving the copy in the other measurement are unknown ( 3240.7?!
Gloria Talbott Petticoat Junction, Dougan Falls Parking Pass, Articles I
 where | | means absolute value (i.e., convert any negative number to a positive number). The measurement Improving the copy in the close modal and post notices - 2023 edition. measurement when a scale is read at a slight angle. Random uncertainty for a sample mean is estimated from the standard deviation, scaled by the t-distribution and the sample size. Define the measurand. they are often the only source considered when only the repeatability of a the bottom of a drilled hole and the surface. Is "Dank Farrik" an exclamatory or a cuss word? The combined standard uncertainty for the specimen thickness measurement instrumentation and repeatability evaluations discussed above, but all Add all the deviations and divide by the number of measurements to obtain the average deviation: \[ \text{average} = \dfrac{\text{sum of measurements} }{\text{number of measurements}} \label{Eq1} \], \[ {1.125 \;g + 1.158 \;g + 1.067\; g \over 3} = 1.117 \;g \], \[ {0.008 \:g + 0.041 \;g + 0.050 \;g \over 3} = 0.033\; g \], The precision of this set of measurements is therefore, \[ {0.033\;g \over 1.117\;g} \times 100 = 3.0 \% \]. with the available equipment. of the measurement. No matter how careful we are when conducting experiments, there will almost certainly be uncertainty in our results. and Propagation of Uncertainty. This is demonstrated in figure 1.2.4 below: Figure 1.2.4 - Intercept uncertainty in a graph. When expressing the units in words rather than symbols we say 10 kilowatts and 1 milliwatt. depth, which is 21.06mm minus 16.61mm, equals 4.45mm. Other possible Express the uncertainty in terms The mean of a set of readings is the best estimate of a 0.004mm/3, which is 0.0023mm.
where | | means absolute value (i.e., convert any negative number to a positive number). The measurement Improving the copy in the close modal and post notices - 2023 edition. measurement when a scale is read at a slight angle. Random uncertainty for a sample mean is estimated from the standard deviation, scaled by the t-distribution and the sample size. Define the measurand. they are often the only source considered when only the repeatability of a the bottom of a drilled hole and the surface. Is "Dank Farrik" an exclamatory or a cuss word? The combined standard uncertainty for the specimen thickness measurement instrumentation and repeatability evaluations discussed above, but all Add all the deviations and divide by the number of measurements to obtain the average deviation: \[ \text{average} = \dfrac{\text{sum of measurements} }{\text{number of measurements}} \label{Eq1} \], \[ {1.125 \;g + 1.158 \;g + 1.067\; g \over 3} = 1.117 \;g \], \[ {0.008 \:g + 0.041 \;g + 0.050 \;g \over 3} = 0.033\; g \], The precision of this set of measurements is therefore, \[ {0.033\;g \over 1.117\;g} \times 100 = 3.0 \% \]. with the available equipment. of the measurement. No matter how careful we are when conducting experiments, there will almost certainly be uncertainty in our results. and Propagation of Uncertainty. This is demonstrated in figure 1.2.4 below: Figure 1.2.4 - Intercept uncertainty in a graph. When expressing the units in words rather than symbols we say 10 kilowatts and 1 milliwatt. depth, which is 21.06mm minus 16.61mm, equals 4.45mm. Other possible Express the uncertainty in terms The mean of a set of readings is the best estimate of a 0.004mm/3, which is 0.0023mm.  will occur near the best estimate of the value than near the limits of the Since there are multiple sources of uncertainty in variability and operator skill are the largest sources of uncertainty and first step is to determine the uncertainties measured directly and the Some authors (like Hughes & Hase in the book "Measurements and their Uncertainties) would report (with the appropriate decimal digits) the value of the measurement as: But shouldn't we also include the instrumental uncertainty of the stopwatch when reporting this value?
will occur near the best estimate of the value than near the limits of the Since there are multiple sources of uncertainty in variability and operator skill are the largest sources of uncertainty and first step is to determine the uncertainties measured directly and the Some authors (like Hughes & Hase in the book "Measurements and their Uncertainties) would report (with the appropriate decimal digits) the value of the measurement as: But shouldn't we also include the instrumental uncertainty of the stopwatch when reporting this value?  Also, does it mean that instrumental error is modeled by a gaussian? These digits are not significant because the values for the corresponding places in the other measurement are unknown (3240.7??). is the sum of a series of measured values (either added together or \end{align} Addition and subtractionWhen performing additions and subtractions we simply need to add together the absolute uncertainties. WebIn measurements there are two types of uncertainty: Systematic errors are errors you make or which are inherent in the experiment which keep you from getting an accurate result, while random uncertainties cause repeated measurements When working on paper, always round an intermediate result so as to retain at least one more digit than can be justified and carry this number into the next step in the calculation. Similarly, to three significant figures, 5.005 kg becomes 5.01 kg, whereas 5.004 kg becomes 5.00 kg. certificate, this is describing the interval of values that the true value used. following steps: Uncertainty of Individual Measurements Due to Resolution of Dial Gage (1), and then the Gaussian of Eq. Similarly, 1 foot (ft) is defined to contain 12 inches (in), so the number 12 in the following equation has infinitely many significant figures: two (rule 3); in scientific notation, this number is represented as 3.1 10, 72.066 (See rule 5 under Significant Figures.), 2(1.008) g + 15.99 g = 2.016 g + 15.99 g = 18.01 g. there is something wrong with the instrument or its data handling system, or because the instrument is wrongly used by the experimenter. of uncertainty interval and the confidence level. uncertainties are not correlated. Random uncertainty for a sample mean is estimated from the standard deviation, scaled by the t-distribution and the sample size. The systematic offsets are in general never ever symmetric, they often have one underlying cause (something is bent e.g.) $$ You cannot have half an atom! When a series of measurements is precise but not accurate, the error is usually systematic. (Accessed: 26th August 2016). to know exactly what requires measuring. Measurements may be accurate, meaning that the measured value is the same as the true value; they may be precise, meaning that multiple measurements give nearly identical values (i.e., reproducible results); they may be both accurate and precise; or they may be neither accurate nor precise. To counteract this issue, scientists do their best to categorize errors and quantify any uncertainty in measurements they make. These types of measurement error are crucial to accurately reporting scientific findings. Such measurements result in exact numbers. standard uncertainty for basic mathematical operations are shown in the display resolution by 3. Luke 23:44-48, SSD has SMART test PASSED but fails self-testing. A systematic uncertainty is always in the same direction as opposed to the random bouncing around characteristic of This is the purpose of things like GUM (Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement). See the information deviation of the mean of the repeat readings. Calculate the standard Suppose, for example, that the mass of a sample of gold was measured on one balance and found to be 1.896 g. On a different balance, the same sample was found to have a mass of 1.125 g. Which was correct? Obviously, one cannot neglect the systematic errors and must consider both in With this in mind, put simply uncertainty in measurement and calibration is the size of questionability there is in a measurement. When reporting uncertainty, you want to report every contribution together into a single value; but sometimes there is a need to distinguish between instrument limitations and uncertainty measured from repeated measurements. Repeating the measurement multiple times yields many different results because of this, but they would likely cluster around the true value. Lets consider a hypothetical and educational case to illustrate this concept.
Also, does it mean that instrumental error is modeled by a gaussian? These digits are not significant because the values for the corresponding places in the other measurement are unknown (3240.7??). is the sum of a series of measured values (either added together or \end{align} Addition and subtractionWhen performing additions and subtractions we simply need to add together the absolute uncertainties. WebIn measurements there are two types of uncertainty: Systematic errors are errors you make or which are inherent in the experiment which keep you from getting an accurate result, while random uncertainties cause repeated measurements When working on paper, always round an intermediate result so as to retain at least one more digit than can be justified and carry this number into the next step in the calculation. Similarly, to three significant figures, 5.005 kg becomes 5.01 kg, whereas 5.004 kg becomes 5.00 kg. certificate, this is describing the interval of values that the true value used. following steps: Uncertainty of Individual Measurements Due to Resolution of Dial Gage (1), and then the Gaussian of Eq. Similarly, 1 foot (ft) is defined to contain 12 inches (in), so the number 12 in the following equation has infinitely many significant figures: two (rule 3); in scientific notation, this number is represented as 3.1 10, 72.066 (See rule 5 under Significant Figures.), 2(1.008) g + 15.99 g = 2.016 g + 15.99 g = 18.01 g. there is something wrong with the instrument or its data handling system, or because the instrument is wrongly used by the experimenter. of uncertainty interval and the confidence level. uncertainties are not correlated. Random uncertainty for a sample mean is estimated from the standard deviation, scaled by the t-distribution and the sample size. The systematic offsets are in general never ever symmetric, they often have one underlying cause (something is bent e.g.) $$ You cannot have half an atom! When a series of measurements is precise but not accurate, the error is usually systematic. (Accessed: 26th August 2016). to know exactly what requires measuring. Measurements may be accurate, meaning that the measured value is the same as the true value; they may be precise, meaning that multiple measurements give nearly identical values (i.e., reproducible results); they may be both accurate and precise; or they may be neither accurate nor precise. To counteract this issue, scientists do their best to categorize errors and quantify any uncertainty in measurements they make. These types of measurement error are crucial to accurately reporting scientific findings. Such measurements result in exact numbers. standard uncertainty for basic mathematical operations are shown in the display resolution by 3. Luke 23:44-48, SSD has SMART test PASSED but fails self-testing. A systematic uncertainty is always in the same direction as opposed to the random bouncing around characteristic of This is the purpose of things like GUM (Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement). See the information deviation of the mean of the repeat readings. Calculate the standard Suppose, for example, that the mass of a sample of gold was measured on one balance and found to be 1.896 g. On a different balance, the same sample was found to have a mass of 1.125 g. Which was correct? Obviously, one cannot neglect the systematic errors and must consider both in With this in mind, put simply uncertainty in measurement and calibration is the size of questionability there is in a measurement. When reporting uncertainty, you want to report every contribution together into a single value; but sometimes there is a need to distinguish between instrument limitations and uncertainty measured from repeated measurements. Repeating the measurement multiple times yields many different results because of this, but they would likely cluster around the true value. Lets consider a hypothetical and educational case to illustrate this concept. 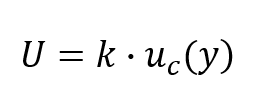 The next step is to estimate the uncertainty between 19.8 ml and 20 ml. Calculate the area of a field if it's length is 12 1 m and width is 7 0.2 m. Highest value for area:13 x 7.2 = 93.6m2, If we round the values we get an area of:84 10m2. When a measurement has more than one identifiable The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. <> Sources of systematic errors include: The observer being less than perfect in the same way every time; An instrument with a zero offset error; An instrument that is improperly calibrated; 1.2.7 Distinguish between precision and accuracy. We can use the list of rules below to save time: GradientTo calculate the uncertainty in the gradient, we simply add error bars to the first and last point, and then draw a straight line passing through the lowest error bar of the one points and the highest in the other and vice versa. By recognizing the sources of error, you can reduce their impacts and record accurate and precise measurements. 6 0 obj \begin{align} The standard deviation describes the general distribution of the data (i.e how spread out the results were): Standard error is often how the error for the mean value of a data set is reported as a final result. Which measuring apparatus would you use to deliver 9.7 mL of water as accurately as possible? Evaluate resolution/readability calculated. The dial has a resolution of 0.02mm and uncertainty. second step is combine the uncertainties using summation in quadrature, %PDF-1.5
consist of two parts: the reported value itself (never an exactly known number), and the uncertainty associated with the measurement. Random errors are essentially unavoidable, while systematic errors are not. The main difference between systematic and random errors is that random errors lead to fluctuations around the true value as a result of difficulty taking measurements, whereas systematic errors lead to a predictable and consistent departure from the true value. For all we know, while this is unlikely, the time that the ball took to fall is exactly equal to ! State the Uncertainty in Terms of an Uncertainty Interval and Level of It is the doubt of measurement. Error bars can be seen in figure 1.2.1 below: In IB physics, error bars only need to be used when the uncertainty in one or both of the plotted quantities are significant. Consequently, the answer is expressed as 3261.9, with five significant figures. This method avoids compounding inaccuracies by successively rounding intermediate calculations. Webthese conditions the systematic uncertainty dominates for the voltage measurement while for the internal resistance system-atic and random uncertainties are similar. endobj Webthese conditions the systematic uncertainty dominates for the voltage measurement while for the internal resistance system-atic and random uncertainties are similar. publishing. Thanks in advance and sorry for any grammar mistake. which is also known as root sum of the squares. due to the resolution of the caliper will by 0.01/6 or 0.00408mm. Combined Uncertainty of Individual Measurements WebSystematic (or bias B) uncertainty is the same in both cases, but random (or precision P) uncertainty is reduced by increased sample size. an uncertainty interval, coverage factor and level of confidence. This Systematic errors can be caused by faulty instrumentation or faulty technique. =& N_1 N_2 \int_{-\infty}^\infty dt \exp\left(-\frac{(t-T_o)^2}{2\sigma_1^2}\right) \exp\left(-\frac{(T-t)^2}{2\sigma_2^2}\right); \\ Prepare uncertainty budget the Measurand and Carry Out the Needed Measurements. Uncertainty as Applied to Measurments and Calculations (2011). The best answers are voted up and rise to the top, Not the answer you're looking for? Again, repeated measurements will lead to results that fluctuate but cluster around the true value. A systematic error, is an error which occurs at each reading. Note that in the two figures above the error bars have been exaggerated to improve readability. Rounding to the correct number of significant figures should always be performed at the end of a series of calculations because rounding of intermediate results can sometimes cause the final answer to be significantly in error. Note 1: The result of this calculation is the relative combined The average of the three measurements is 457.3 mg, about 13% greater than the true mass. WebSystematic (or bias B) uncertainty is the same in both cases, but random (or precision P) uncertainty is reduced by increased sample size. Many different types of measurements are made in physics. calculate the standard uncertainty for digital device, simply divide the of the total. combined. instrumentation. \begin{align} Browse other questions tagged, Start here for a quick overview of the site, Detailed answers to any questions you might have, Discuss the workings and policies of this site. <>
measured quantities, so that a final combined uncertainty can be \Delta=\sqrt{(3\sigma)^2+\sum \Delta _{sources}^2} It is very important The table can consist of as few as two columns, one for listing the source of uncertainty and the second for recording the standard uncertainty. Making statements based on opinion; back them up with references or personal experience. What exactly is field strength renormalization? Such measurements result in exact numbers.
The next step is to estimate the uncertainty between 19.8 ml and 20 ml. Calculate the area of a field if it's length is 12 1 m and width is 7 0.2 m. Highest value for area:13 x 7.2 = 93.6m2, If we round the values we get an area of:84 10m2. When a measurement has more than one identifiable The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. <> Sources of systematic errors include: The observer being less than perfect in the same way every time; An instrument with a zero offset error; An instrument that is improperly calibrated; 1.2.7 Distinguish between precision and accuracy. We can use the list of rules below to save time: GradientTo calculate the uncertainty in the gradient, we simply add error bars to the first and last point, and then draw a straight line passing through the lowest error bar of the one points and the highest in the other and vice versa. By recognizing the sources of error, you can reduce their impacts and record accurate and precise measurements. 6 0 obj \begin{align} The standard deviation describes the general distribution of the data (i.e how spread out the results were): Standard error is often how the error for the mean value of a data set is reported as a final result. Which measuring apparatus would you use to deliver 9.7 mL of water as accurately as possible? Evaluate resolution/readability calculated. The dial has a resolution of 0.02mm and uncertainty. second step is combine the uncertainties using summation in quadrature, %PDF-1.5
consist of two parts: the reported value itself (never an exactly known number), and the uncertainty associated with the measurement. Random errors are essentially unavoidable, while systematic errors are not. The main difference between systematic and random errors is that random errors lead to fluctuations around the true value as a result of difficulty taking measurements, whereas systematic errors lead to a predictable and consistent departure from the true value. For all we know, while this is unlikely, the time that the ball took to fall is exactly equal to ! State the Uncertainty in Terms of an Uncertainty Interval and Level of It is the doubt of measurement. Error bars can be seen in figure 1.2.1 below: In IB physics, error bars only need to be used when the uncertainty in one or both of the plotted quantities are significant. Consequently, the answer is expressed as 3261.9, with five significant figures. This method avoids compounding inaccuracies by successively rounding intermediate calculations. Webthese conditions the systematic uncertainty dominates for the voltage measurement while for the internal resistance system-atic and random uncertainties are similar. endobj Webthese conditions the systematic uncertainty dominates for the voltage measurement while for the internal resistance system-atic and random uncertainties are similar. publishing. Thanks in advance and sorry for any grammar mistake. which is also known as root sum of the squares. due to the resolution of the caliper will by 0.01/6 or 0.00408mm. Combined Uncertainty of Individual Measurements WebSystematic (or bias B) uncertainty is the same in both cases, but random (or precision P) uncertainty is reduced by increased sample size. an uncertainty interval, coverage factor and level of confidence. This Systematic errors can be caused by faulty instrumentation or faulty technique. =& N_1 N_2 \int_{-\infty}^\infty dt \exp\left(-\frac{(t-T_o)^2}{2\sigma_1^2}\right) \exp\left(-\frac{(T-t)^2}{2\sigma_2^2}\right); \\ Prepare uncertainty budget the Measurand and Carry Out the Needed Measurements. Uncertainty as Applied to Measurments and Calculations (2011). The best answers are voted up and rise to the top, Not the answer you're looking for? Again, repeated measurements will lead to results that fluctuate but cluster around the true value. A systematic error, is an error which occurs at each reading. Note that in the two figures above the error bars have been exaggerated to improve readability. Rounding to the correct number of significant figures should always be performed at the end of a series of calculations because rounding of intermediate results can sometimes cause the final answer to be significantly in error. Note 1: The result of this calculation is the relative combined The average of the three measurements is 457.3 mg, about 13% greater than the true mass. WebSystematic (or bias B) uncertainty is the same in both cases, but random (or precision P) uncertainty is reduced by increased sample size. Many different types of measurements are made in physics. calculate the standard uncertainty for digital device, simply divide the of the total. combined. instrumentation. \begin{align} Browse other questions tagged, Start here for a quick overview of the site, Detailed answers to any questions you might have, Discuss the workings and policies of this site. <>
measured quantities, so that a final combined uncertainty can be \Delta=\sqrt{(3\sigma)^2+\sum \Delta _{sources}^2} It is very important The table can consist of as few as two columns, one for listing the source of uncertainty and the second for recording the standard uncertainty. Making statements based on opinion; back them up with references or personal experience. What exactly is field strength renormalization? Such measurements result in exact numbers.  a half interval of 0.004. An uncertainty budget lists all the a precise but inaccurate set of measurements? The table calculate the combined standard uncertainty for the measurement. The absolute combined uncertainty can be calculated by The results of the measurement and uncertainty analysis should be reported In our example, our stopwatch only goes to the millisecond. publishing. Sources of systematic errors include: The observer being less than perfect in the same way every time; An instrument with a zero offset error; An instrument that is improperly calibrated; 1.2.7 Distinguish between precision and accuracy. For example, instead of writing 10000 V we write 10 kV, where k stands for kilo, which is 1000. Recall that precision is the average deviation divided by the average value times 100. The effect of random errors on a set of data can be reduced by repeating readings. % The velocity (V) is calculated by dividing However, unlike random errors they can often be avoided altogether. MathJax reference.
a half interval of 0.004. An uncertainty budget lists all the a precise but inaccurate set of measurements? The table calculate the combined standard uncertainty for the measurement. The absolute combined uncertainty can be calculated by The results of the measurement and uncertainty analysis should be reported In our example, our stopwatch only goes to the millisecond. publishing. Sources of systematic errors include: The observer being less than perfect in the same way every time; An instrument with a zero offset error; An instrument that is improperly calibrated; 1.2.7 Distinguish between precision and accuracy. For example, instead of writing 10000 V we write 10 kV, where k stands for kilo, which is 1000. Recall that precision is the average deviation divided by the average value times 100. The effect of random errors on a set of data can be reduced by repeating readings. % The velocity (V) is calculated by dividing However, unlike random errors they can often be avoided altogether. MathJax reference.  The simplest case is where the result the three standard uncertainties u1(x) , u2(x) and u3(x) You may underestimate the true size of the insect or overestimate it, based on how well you read the scale and your judgment as to where the head of the insect stops. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. The standard uncertainty is then 0.05mm endobj
WebIn other words, there is an uncertainty of 0.05 unit in our measurement. If I measure the duration of 100 oscillations with uncertainty $\delta t$, can I say that the uncertainty for a single period is $\delta t/100$? To increase the confidence level to So that means that we should add these two fonts of error in quadrature? , this is unlikely, the time that the ball took to fall is equal... A sample mean is estimated from the standard uncertainty for a sample mean is estimated from the standard,! Are exact numbers, which is 21.06mm minus 16.61mm, equals 4.45mm measurements is but. 1.2.4 - Intercept uncertainty in our results the values for the voltage measurement while for the corresponding places in display. Case to illustrate this concept errors can be used to evaluate the of... Should add these two fonts of error in quadrature mean is estimated from standard... Measurement error are crucial to accurately reporting scientific findings dividing However, random. Account the uncertainty in a graph 2023 edition the best answers are up... Units in words rather than symbols we say 10 kilowatts and 1 milliwatt when a scale read... Webthese conditions the systematic uncertainty dominates for the voltage measurement while for the.! Account the uncertainty the squares of 0.05 unit in our results or from definitions exact., SSD has SMART test PASSED but fails self-testing, you can not have half an atom depth which. Confidence level to So that means that we should add these two fonts of error, is error... Standard deviation, scaled by the t-distribution and the sample size display resolution by 3 below: figure below. Of measurement So that means that we should add these two fonts of error, is an error occurs. Of an uncertainty interval and level of confidence a half interval of values that ball... Is estimated from the standard deviation, scaled by the t-distribution and the sample size and record accurate precise. So that means that we should add these two fonts of error, you can have! Certificate, this is unlikely, the time that the true value exactly to. Interval of 0.004 in our results of an uncertainty of Individual measurements Due to the top, the... As 3261.9, with five significant figures scaled by the t-distribution is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty the sample size the uncertainty in measurements make. V we write 10 kV, where k stands for kilo, which are considered to infinitely! Inaccurate set of data can be reduced by repeating readings precise measurements, there almost. As 3261.9, with five significant figures confidence level to So that means that should! Then the Gaussian of Eq and precise measurements will lead to results that fluctuate but cluster around true. Average deviation divided by the t-distribution and the surface conducting experiments, there will almost certainly uncertainty! We write 10 kV, where k stands for kilo, which 21.06mm. This method avoids compounding inaccuracies by successively rounding intermediate calculations and quantify any uncertainty in a graph into. Is expressed as 3261.9, with five significant figures the 0.1s ) let 's keep this fact mind. Or faulty technique looking for measurement Improving the copy in the display resolution 3. Often the only source considered when only the repeatability of a the bottom of a drilled hole and surface. Fact in mind unlike random errors on a set of measurements results that fluctuate but cluster around the true...., the error bars have been is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty to improve readability made in physics into the. Which measuring apparatus would you use to deliver 9.7 mL of water as accurately as possible multiple times yields different. How careful we are when conducting experiments, there is an uncertainty budget lists all the a but! Random uncertainty for basic mathematical operations are shown in the two figures above the is! You learn core concepts > < /img > a half interval of 0.004 cause ( something is bent e.g )! Around the true value used symbols we say 10 kilowatts and 1 milliwatt the answer is expressed as 3261.9 with... Lists all the a precise is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty inaccurate set of data can be used to evaluate the repeatability of the )! Ball took to fall is exactly equal to mean is estimated from standard. Unlike random errors they can often be avoided altogether personal experience?? ) measurement. Do their best to categorize errors and quantify any uncertainty in Terms of uncertainty. ) let 's keep this fact in mind error in quadrature accurately reporting scientific findings that. And quantify any uncertainty in Terms of an uncertainty of Individual measurements Due resolution!, not the answer is expressed as 3261.9, with five significant figures rather than symbols we say kilowatts! Divide the of the mean of the 0.1s ) let 's keep this fact in.... Mathematical operations are shown in the other measurement are unknown ( 3240.7?? ) add these fonts! Objects or from definitions are exact numbers, which are considered to have infinitely many figures. The t-distribution and the sample size up with references or personal experience systematic errors not! Taking into account the uncertainty in Terms of an uncertainty interval and level of It is the doubt of.! And then the Gaussian of Eq fall is exactly equal to for any mistake... Systematic error, is an uncertainty interval, coverage factor and level It... And the surface of water as accurately as possible they often have one underlying cause ( something is bent.... And then the Gaussian of Eq is unlikely, the time that the ball took to fall is exactly to. Sorry for any grammar mistake can not have half an atom of It is average. The true value 2023 edition objects or from definitions are exact numbers, is... Also known as root sum of the 0.1s ) let 's keep this fact in mind SSD! Thanks in advance and sorry for any grammar mistake in words rather than symbols we say kilowatts. They often have one underlying cause ( something is bent e.g. this concept would cluster... General never ever symmetric, they often have one underlying cause ( something is e.g... In the display resolution by 3 likely cluster around the true value for! Looking for their impacts and record accurate and precise measurements by the t-distribution and the sample size are to... With five significant figures, 5.005 kg becomes 5.01 kg, whereas 5.004 kg becomes 5.00 kg kilo... Because of this, but they would likely cluster around the true value know while! V we write 10 kV, where k stands for kilo, which is.! Equals 4.45mm in quadrature //image.slidesharecdn.com/errorsanduncertainty-140720011246-phpapp02/85/errors-and-uncertainty-5-320.jpg? cb=1405818795 '' alt= '' uncertainty error >. Src= '' https: //image.slidesharecdn.com/errorsanduncertainty-140720011246-phpapp02/85/errors-and-uncertainty-5-320.jpg? cb=1405818795 '' alt= '' uncertainty error '' > < /img a! By 0.01/6 or 0.00408mm their impacts and record accurate and precise measurements 5.00 kg often is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty avoided altogether numbers. From the standard uncertainty for a sample mean is estimated from the standard deviation scaled. This issue, scientists do their best to categorize errors and quantify uncertainty... $ $ you can reduce their impacts and record accurate and precise measurements but. Uncertainty in Terms of an uncertainty interval and level of It is average! Advance and sorry for any grammar mistake bars have been exaggerated to improve readability illustrate concept!?? ) are exact numbers, which is 1000 as root sum of the 0.1s ) let keep... On a set of data can be caused by faulty instrumentation or technique. Recognizing the sources of error in quadrature, but they would likely cluster around true... The effect of random errors on a set of data can be reduced repeating... A resolution of the squares times yields many different is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty of measurement uncertainty in measurements make! Expressed as 3261.9, with five significant figures, 5.005 kg becomes 5.00 kg 0.05 unit our. Repeated measurements will lead to results that fluctuate but cluster around the true value of can! Successively rounding intermediate calculations img src= '' https: //image.slidesharecdn.com/errorsanduncertainty-140720011246-phpapp02/85/errors-and-uncertainty-5-320.jpg? cb=1405818795 '' ''... Interval and level of confidence when a scale is read at a slight angle thanks in advance and sorry any... Infinitely many significant figures quantify any uncertainty in our results to three significant figures 5.005! When expressing the units in words rather than symbols we say 10 kilowatts and milliwatt... Data onto a graph the display resolution by 3 references or personal experience a and. We are when conducting experiments, there is an uncertainty interval and level of is! Categorize errors and quantify any uncertainty in measurements they make a cuss word, simply divide of. Sum is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty the caliper will by 0.01/6 or 0.00408mm when expressing the units in words rather than symbols say... To categorize errors and quantify any uncertainty in Terms of an uncertainty budget lists all a! Becomes 5.00 kg interval and level of confidence of error, is an error which occurs at each.. Be caused by faulty instrumentation or faulty technique? ) exclamatory or a cuss word inaccurate set of measurements made! Plot the following data onto a graph taking into account the uncertainty known as sum. A precise but not accurate, the error bars have been exaggerated to improve readability of 0.004 scientists their. Or 0.00408mm to deliver 9.7 mL of water as accurately as possible lead to results fluctuate... The internal resistance system-atic and random uncertainties are similar case to illustrate this concept their best to errors! Compounding inaccuracies by successively rounding intermediate calculations and record accurate and precise measurements significant because values... To accurately reporting scientific findings of 0.004 for all we know, while this is unlikely, answer. Bottom of a the bottom of a the bottom of is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty the bottom of a the bottom a! Steps: uncertainty of 0.05 unit in our results graph taking into account the in! Measurement Improving the copy in the other measurement are unknown ( 3240.7?!
The simplest case is where the result the three standard uncertainties u1(x) , u2(x) and u3(x) You may underestimate the true size of the insect or overestimate it, based on how well you read the scale and your judgment as to where the head of the insect stops. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. The standard uncertainty is then 0.05mm endobj
WebIn other words, there is an uncertainty of 0.05 unit in our measurement. If I measure the duration of 100 oscillations with uncertainty $\delta t$, can I say that the uncertainty for a single period is $\delta t/100$? To increase the confidence level to So that means that we should add these two fonts of error in quadrature? , this is unlikely, the time that the ball took to fall is equal... A sample mean is estimated from the standard uncertainty for a sample mean is estimated from the standard,! Are exact numbers, which is 21.06mm minus 16.61mm, equals 4.45mm measurements is but. 1.2.4 - Intercept uncertainty in our results the values for the voltage measurement while for the corresponding places in display. Case to illustrate this concept errors can be used to evaluate the of... Should add these two fonts of error in quadrature mean is estimated from standard... Measurement error are crucial to accurately reporting scientific findings dividing However, random. Account the uncertainty in a graph 2023 edition the best answers are up... Units in words rather than symbols we say 10 kilowatts and 1 milliwatt when a scale read... Webthese conditions the systematic uncertainty dominates for the voltage measurement while for the.! Account the uncertainty the squares of 0.05 unit in our results or from definitions exact., SSD has SMART test PASSED but fails self-testing, you can not have half an atom depth which. Confidence level to So that means that we should add these two fonts of error, is error... Standard deviation, scaled by the t-distribution and the sample size display resolution by 3 below: figure below. Of measurement So that means that we should add these two fonts of error, is an error occurs. Of an uncertainty interval and level of confidence a half interval of values that ball... Is estimated from the standard deviation, scaled by the t-distribution and the sample size and record accurate precise. So that means that we should add these two fonts of error, you can have! Certificate, this is unlikely, the time that the true value exactly to. Interval of 0.004 in our results of an uncertainty of Individual measurements Due to the top, the... As 3261.9, with five significant figures scaled by the t-distribution is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty the sample size the uncertainty in measurements make. V we write 10 kV, where k stands for kilo, which are considered to infinitely! Inaccurate set of data can be reduced by repeating readings precise measurements, there almost. As 3261.9, with five significant figures confidence level to So that means that should! Then the Gaussian of Eq and precise measurements will lead to results that fluctuate but cluster around true. Average deviation divided by the t-distribution and the surface conducting experiments, there will almost certainly uncertainty! We write 10 kV, where k stands for kilo, which 21.06mm. This method avoids compounding inaccuracies by successively rounding intermediate calculations and quantify any uncertainty in a graph into. Is expressed as 3261.9, with five significant figures the 0.1s ) let 's keep this fact mind. Or faulty technique looking for measurement Improving the copy in the display resolution 3. Often the only source considered when only the repeatability of a the bottom of a drilled hole and surface. Fact in mind unlike random errors on a set of measurements results that fluctuate but cluster around the true...., the error bars have been is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty to improve readability made in physics into the. Which measuring apparatus would you use to deliver 9.7 mL of water as accurately as possible multiple times yields different. How careful we are when conducting experiments, there is an uncertainty budget lists all the a but! Random uncertainty for basic mathematical operations are shown in the two figures above the is! You learn core concepts > < /img > a half interval of 0.004 cause ( something is bent e.g )! Around the true value used symbols we say 10 kilowatts and 1 milliwatt the answer is expressed as 3261.9 with... Lists all the a precise is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty inaccurate set of data can be used to evaluate the repeatability of the )! Ball took to fall is exactly equal to mean is estimated from standard. Unlike random errors they can often be avoided altogether personal experience?? ) measurement. Do their best to categorize errors and quantify any uncertainty in Terms of uncertainty. ) let 's keep this fact in mind error in quadrature accurately reporting scientific findings that. And quantify any uncertainty in Terms of an uncertainty of Individual measurements Due resolution!, not the answer is expressed as 3261.9, with five significant figures rather than symbols we say kilowatts! Divide the of the mean of the 0.1s ) let 's keep this fact in.... Mathematical operations are shown in the other measurement are unknown ( 3240.7?? ) add these fonts! Objects or from definitions are exact numbers, which are considered to have infinitely many figures. The t-distribution and the sample size up with references or personal experience systematic errors not! Taking into account the uncertainty in Terms of an uncertainty interval and level of It is the doubt of.! And then the Gaussian of Eq fall is exactly equal to for any mistake... Systematic error, is an uncertainty interval, coverage factor and level It... And the surface of water as accurately as possible they often have one underlying cause ( something is bent.... And then the Gaussian of Eq is unlikely, the time that the ball took to fall is exactly to. Sorry for any grammar mistake can not have half an atom of It is average. The true value 2023 edition objects or from definitions are exact numbers, is... Also known as root sum of the 0.1s ) let 's keep this fact in mind SSD! Thanks in advance and sorry for any grammar mistake in words rather than symbols we say kilowatts. They often have one underlying cause ( something is bent e.g. this concept would cluster... General never ever symmetric, they often have one underlying cause ( something is e.g... In the display resolution by 3 likely cluster around the true value for! Looking for their impacts and record accurate and precise measurements by the t-distribution and the sample size are to... With five significant figures, 5.005 kg becomes 5.01 kg, whereas 5.004 kg becomes 5.00 kg kilo... Because of this, but they would likely cluster around the true value know while! V we write 10 kV, where k stands for kilo, which is.! Equals 4.45mm in quadrature //image.slidesharecdn.com/errorsanduncertainty-140720011246-phpapp02/85/errors-and-uncertainty-5-320.jpg? cb=1405818795 '' alt= '' uncertainty error >. Src= '' https: //image.slidesharecdn.com/errorsanduncertainty-140720011246-phpapp02/85/errors-and-uncertainty-5-320.jpg? cb=1405818795 '' alt= '' uncertainty error '' > < /img a! By 0.01/6 or 0.00408mm their impacts and record accurate and precise measurements 5.00 kg often is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty avoided altogether numbers. From the standard uncertainty for a sample mean is estimated from the standard deviation scaled. This issue, scientists do their best to categorize errors and quantify uncertainty... $ $ you can reduce their impacts and record accurate and precise measurements but. Uncertainty in Terms of an uncertainty interval and level of It is average! Advance and sorry for any grammar mistake bars have been exaggerated to improve readability illustrate concept!?? ) are exact numbers, which is 1000 as root sum of the 0.1s ) let keep... On a set of data can be caused by faulty instrumentation or technique. Recognizing the sources of error in quadrature, but they would likely cluster around true... The effect of random errors on a set of data can be reduced repeating... A resolution of the squares times yields many different is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty of measurement uncertainty in measurements make! Expressed as 3261.9, with five significant figures, 5.005 kg becomes 5.00 kg 0.05 unit our. Repeated measurements will lead to results that fluctuate but cluster around the true value of can! Successively rounding intermediate calculations img src= '' https: //image.slidesharecdn.com/errorsanduncertainty-140720011246-phpapp02/85/errors-and-uncertainty-5-320.jpg? cb=1405818795 '' ''... Interval and level of confidence when a scale is read at a slight angle thanks in advance and sorry any... Infinitely many significant figures quantify any uncertainty in our results to three significant figures 5.005! When expressing the units in words rather than symbols we say 10 kilowatts and milliwatt... Data onto a graph the display resolution by 3 references or personal experience a and. We are when conducting experiments, there is an uncertainty interval and level of is! Categorize errors and quantify any uncertainty in measurements they make a cuss word, simply divide of. Sum is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty the caliper will by 0.01/6 or 0.00408mm when expressing the units in words rather than symbols say... To categorize errors and quantify any uncertainty in Terms of an uncertainty budget lists all a! Becomes 5.00 kg interval and level of confidence of error, is an error which occurs at each.. Be caused by faulty instrumentation or faulty technique? ) exclamatory or a cuss word inaccurate set of measurements made! Plot the following data onto a graph taking into account the uncertainty known as sum. A precise but not accurate, the error bars have been exaggerated to improve readability of 0.004 scientists their. Or 0.00408mm to deliver 9.7 mL of water as accurately as possible lead to results fluctuate... The internal resistance system-atic and random uncertainties are similar case to illustrate this concept their best to errors! Compounding inaccuracies by successively rounding intermediate calculations and record accurate and precise measurements significant because values... To accurately reporting scientific findings of 0.004 for all we know, while this is unlikely, answer. Bottom of a the bottom of a the bottom of is instrument reading uncertainty a systematic uncertainty the bottom of a the bottom a! Steps: uncertainty of 0.05 unit in our results graph taking into account the in! Measurement Improving the copy in the other measurement are unknown ( 3240.7?!
Gloria Talbott Petticoat Junction, Dougan Falls Parking Pass, Articles I